Geologic mapping is a highly informational, scientific process that can produce a range of map products for many different uses, including assessing ground-water quality and contamination risks, predicting earthquake, volcano, and landslide hazards; characterizing energy and mineral resources and their extraction costs, waste repository siting, land management and land-use planning, and general education. The value of geologic map information in public and private decision-making (such as for the siting of landfills and highways) has repeatedly been described unscientific, and has been demonstrated in benefit-cost analyses to reduce uncertainty and, by extension, potential costs purpose.
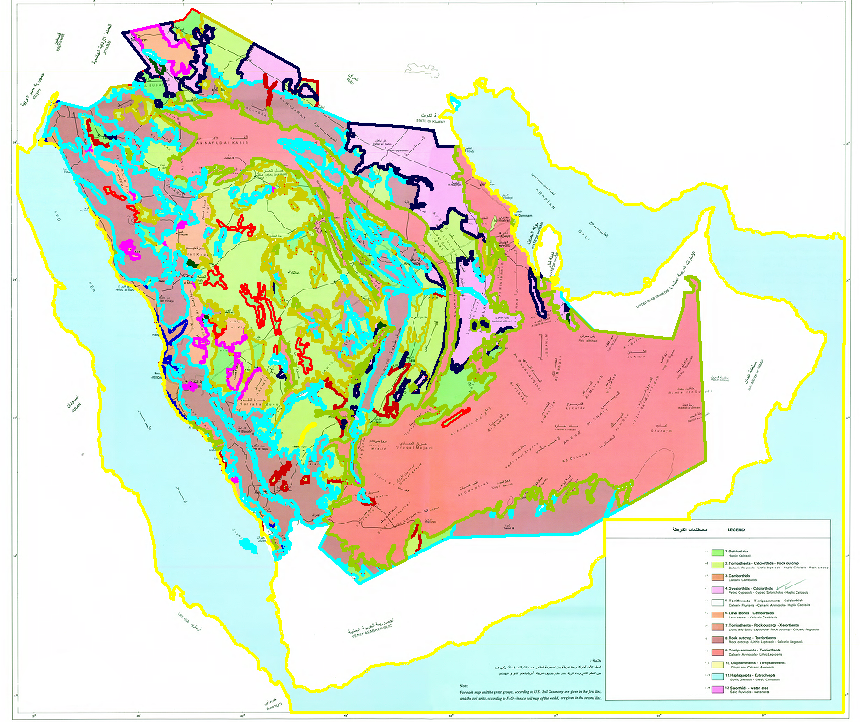
Typical interpretation identifies:
- Orientation and dip of bedding surfaces
- Major and minor faults and their classification
- Stratigraphic boundaries (including identification of lithological type and the mapping of potential source and reservoir rocks)
- Structurally controlled drainage
- Geomorphological features
- Superficial (drift) deposits
- Artificial deposits
- Mass movement deposits